S1ngularity Attack Compromises Nx Build System, Exposing Thousands of Credentials
Developers using the Nx build system are urged to update immediately following a supply chain attack. Malicious versions of the core npm package and related plugins were injected, potentially harvesting over 2,300 GitHub, cloud, and AI credentials from unsuspecting users.
The team behind the 'nx' build system is sounding the alarm about a supply chain attack. Attackers managed to sneak malicious code into the popular npm package, as well as some related plugins. The scary part? This code was designed to steal your data.
"Malicious versions of the nx package... contained code that scans the file system, collects credentials, and posts them to GitHub as a repo under the user's accounts," the maintainers warned in a security advisory.
So, what is 'nx'? It's an open-source build platform used to manage codebases. It's even touted as an "AI-first" platform. The npm package is incredibly popular, with over 3.5 million weekly downloads. Big target, right?
Which Packages Were Affected?
Here's the list of compromised packages and their versions. Good news: these have already been removed from the npm registry. The attack happened around August 26, 2025.
- nx 21.5.0, 20.9.0, 20.10.0, 21.6.0, 20.11.0, 21.7.0, 21.8.0, 20.12.0
- @nx/devkit 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/enterprise-cloud 3.2.0
- @nx/eslint 21.5.0
- @nx/js 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/key 3.2.0
- @nx/node 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/workspace 21.5.0, 20.9.0
How Did This Happen? A Flawed Workflow
The root cause? A vulnerable workflow added on August 21, 2025. This introduced a way to inject malicious code using a specially crafted title in a pull request (PR). While the team quickly reverted the workflow in their main branch after realizing the danger, the attackers were able to target an older branch that still had the flaw.
The nx team explained that the "pull_request_target" trigger, meant to run actions when a PR was created or modified, was the problem. This trigger, unlike the standard "pull_request" trigger, runs workflows with elevated permissions. This includes a GITHUB_TOKEN that has read/write access to the repository – a juicy target for attackers.
It's believed that the attackers used this GITHUB_TOKEN to trigger the "publish.yml" workflow, which is responsible for publishing packages to the npm registry.
Basically, the attackers exploited the injection flaw to execute commands and steal the npm token, allowing them to publish the malicious versions of 'nx'.
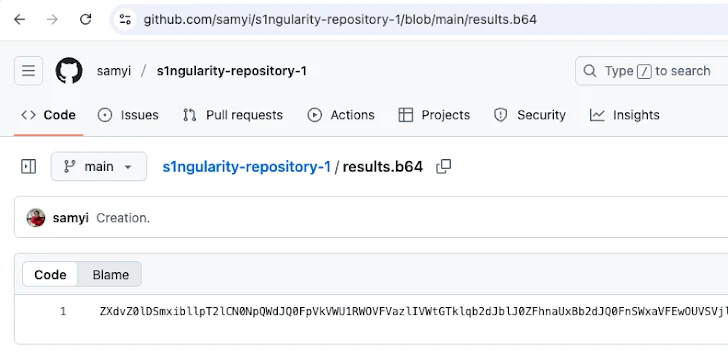
The injected code contained a postinstall script that would activate after installation. This script would scan the system for text files, collect credentials, and send that information as a Base64-encoded string to a GitHub repository named "s1ngularity-repository" (or similar variations) under the user's account. Yikes!
And it gets worse! The malicious script also modified the `.zshrc` and `.bashrc` files (run whenever a terminal is launched) to include `sudo shutdown -h 0`. This would prompt users for their system password and, if entered, immediately shut down the machine.
What Should You Do?
GitHub has started archiving the malicious repositories. But if you find one, assume you've been compromised. Here's what you need to do:
- Rotate your GitHub and npm credentials and tokens immediately.
- Stop using the affected packages.
- Check your `.zshrc` and `.bashrc` files for anything suspicious and remove it.
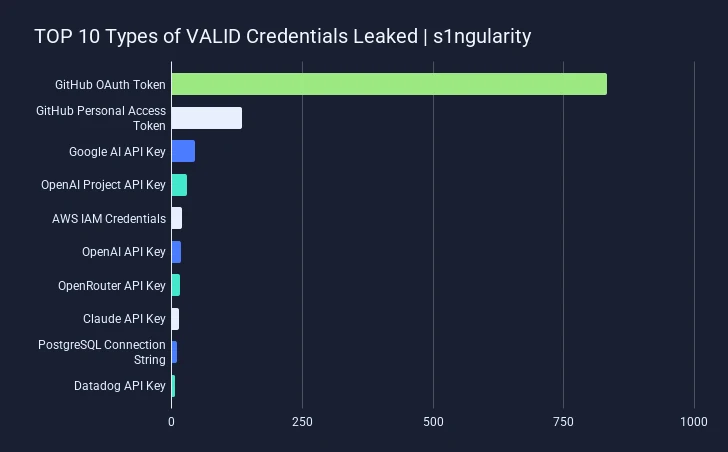
Image Source: GitGuardian
What's Being Done Now?
The nx team has rotated their npm and GitHub tokens, audited activity for anything fishy, and are now requiring two-factor authentication (2FA) for publishing.
Researchers at Wiz found that a staggering 90% of over 1,000 leaked GitHub tokens are still valid, along with many cloud credentials and npm tokens. The malware seems to have spread through developer machines, often via the nx Visual Studio Code extension. GitGuardian has detected over 1,300 repositories with the "s1ngularity-repository" string.
Out of the thousands of secrets leaked, most were GitHub OAuth keys and personal access tokens (PATs), followed by API keys and credentials for services like Google AI, OpenAI, Amazon Web Services, and others.
The attack seems to target Linux and macOS systems, systematically hunting for sensitive files, credentials, SSH keys, and `.gitconfig` files.
Wiz notes that the attackers even weaponized AI CLI tools by using dangerous flags to bypass permissions and steal file system contents, essentially turning trusted tools into malicious reconnaissance agents. Read their full report here.
StepSecurity points out that this is the first time attackers have used developer AI assistants like Claude, Google Gemini, and Amazon Q to exploit the supply chain and bypass security boundaries.
Socket notes some differences between the malware in scoped packages (like @nx/devkit) versus the main nx package, including variations in the AI prompts used to target specific data.
Charlie Eriksen of Aikido also has a write-up on this incident. Stay safe out there!